From - Live Science
By - Skyler Ware
Edited by - Amal Udawatta

Plate tectonics give rise to Earth's mountain ranges, earthquakes and the long-term movement of continents, and may even have provided the right conditions for life on Earth. But as far as we know, no other bodies in the solar system exhibit plate tectonics today. Why is our world different?
"We don't know for sure," Bradford Foley, a geodynamicist at Penn State, told Live Science. "I think it's still considered one of the great unsolved problems in geophysics today."
Earth's lithosphere — its crust and rigid upper mantle — is split into roughly 15 constantly-moving plates. These plates are perpetually shifting, colliding and pulling apart from one another. Though scientists aren't sure how the lithosphere came to be divided into plates, certain aspects of Earth's geology keep the plate tectonic engine chugging along.
For a planet to sustain plate tectonics, it must have a convective mantle, Foley said. Cold, dense surface material sinks back into the mantle at subduction zones, where one plate slips beneath another, and new material rises up where plates spread apart. Without the convective mantle, there wouldn't be enough energy to move the plates.
But convection on its own isn't enough to guarantee that a planet or moon will exhibit plate tectonics. The lithosphere has to be both thin enough to break into plates in the first place and dense enough for those plates to eventually sink into the mantle, said Geoffrey Collins, a geologist at Wheaton College in Massachusetts.
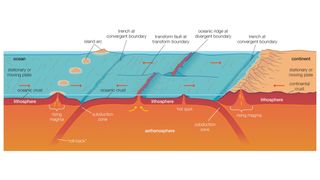
Interactions between plate boundaries and liquid water might also play a role, said Russell Pysklywec, a geophysicist at the University of Toronto. "When we hydrate these rocks and they go down into the Earth, it actually serves to, for lack of a better explanation, lubricate the rocks a little bit more," Pysklywec told Live Science. "It might be that at subduction zones where the two plates are coming together, and with our liquid oceans, we're actually adding that lubricant in that helps facilitate plate tectonics."
The combination of these factors could explain why Earth is the only planet known to exhibit plate tectonics today. In a 2022 study, Collins and his colleagues found that Jupiter's icy moon Europa had exhibited "plate-tectonic-like" activity in the past: Parts of the moon's icy shell were broken into plates that spread and collided. The warmer water beneath the ice may have buoyed those plates along, but because ice is less dense than water, the plates didn't sink into the oceans the same way Earth's plates sink back into the mantle.
Europa's plate-like behavior also doesn't cover the moon's entire surface. "On Europa, it seems to just be patchy, like there's a little patch happening over here, there's a little patch happening over there, and then it doesn't seem to be happening in between," Collins told Live Science. "The other patchiness is that it's patchy in time, so it appears to turn on and off."
Other planets, such as Mars, adopt a "stagnant lid" configuration. These planets have convective mantles, but the surface isn't broken into plates. "Instead of being broken up into these separate plates that move around with that convective mantle, there's one big plate covering the whole planet," Foley said. "It's like a lid on top of its convective mantle."
But without any other nearby planets exhibiting plate tectonics to compare Earth's system to, it's hard to know precisely what causes a planet to develop plate tectonics, Foley said. "If we had hundreds of rocky planets, and all sorts of different conditions, we could probably empirically figure out what the key factors are. But it's hard to do with just one."
Comments
Post a Comment