Aleks Phillips BBC New , Michael Bristow, BBC World Service
Edited by - Amal Udawatta
 US Navy
US NavyThe Royal New Zealand Navy has lost its first ship to the sea since World War Two, after one of its vessels ran aground off the coast of Samoa.
HMNZS Manawanui, a specialist diving and ocean imaging ship, came into trouble about one nautical mile from the island of Upolu on Saturday night local time, while conducting a survey of a reef.
It later caught fire before capsizing.
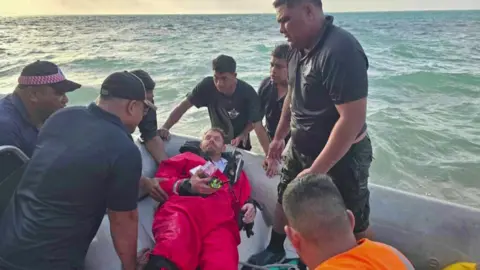
All 75 people on board were evacuated onto lifeboats and rescued early on Sunday, New Zealand's Defence Force said in a statement.
Officials said the cause of the grounding was unknown and will be investigated.
 Reuters
ReutersThe incident occurred during a bout of rough and windy weather.
Military officials said rescuers "battled" currents and winds that pushed life rafts and sea boats towards the reefs, and swells made rescue efforts "challenging".
Officials said the area had not been surveyed since 1987.
The vessel's crew and passengers - including seven scientists and four foreign military personnel - are being accommodated in Samoa before being flown back to New Zealand.
As of 06:40 local time on Sunday (18:40 BST on Saturday), the ship was seen listing heavily with smoke billowing from it.
By 09:00 (21:00 BST on Saturday), it was below the surface.
 Reuters
ReutersDefence minister Judith Collins described the incident as "a really sad day for the Navy" during a news conference.
She added: "But everyone came through, and that, I have to say, is down to the professionalism [of the crew], the training and their own courage."
Dave Poole, who witnessed the ship ablaze, told the Reuters news agency: "As we came into the bay we saw the ship and no smoke. Within 15 minutes fire and smoke were visible. It sank shortly after."
HMNZS Manawanui is the first of New Zealand's naval vessels to be unintentionally sunk since the nation participated in naval battles during World War Two.
Several other ships have been intentionally sunk in the intervening period for various reasons, including to serve as a diving wreck or an artificial reef.
Military officials said their efforts are now turning towards attempting to salvage the vessel and minimising the environmental impacts of the sinking.
 Reuters
Reuters
Comments
Post a Comment