From - Sky & Telescope,
By - Bob King,
Edited by - Amal Udawatta,

Bob King
Astronomical cycles acquaint us with the inevitable. That's what I'm thinking right now as we approach the first official day of fall (spring in the southern hemisphere), also known as the autumnal equinox. At 2:49 a.m. EDT, the Sun will cross the celestial equator going south and won't stop its descent until it bumps into the winter solstice on December 21st.
The celestial equator is a projection of Earth's equator on the sky. On that special day, the Sun will pass directly overhead at noon for residents living along the equator, from Nairobi to Quito to Singapore. At local noon, when the Sun passes overhead, residents won't be able to avoid stepping on their shadows. On the same day at the North and South Poles the Sun scrapes completely around the horizon. And no matter where you live except the poles it rises due east and sets due west.
At both the spring and fall equinoxes, the Earth's axis tilts neither toward nor away from the Sun but sidelong. Day and night momentarily strike a balance, each of them 12 hours long on this day, so neither one of them has the upper hand. That's why we call it the equinox, which literally means "equal night." Right?
Don't believe it. There's more to daylight on the equinox than you might think.
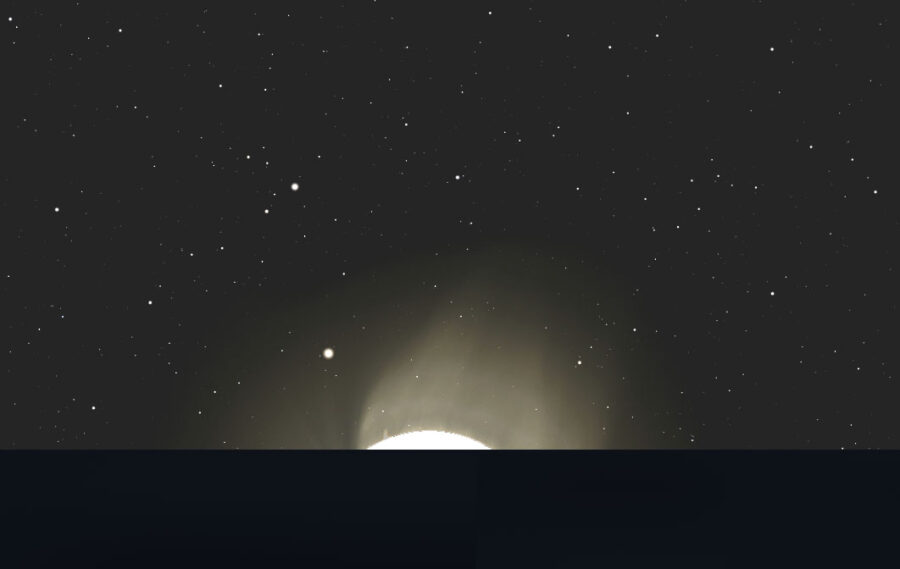
THE SUN'S DISK

Bob King
Even on the equinox, daylight still edges out night for two reasons. First, the Sun is a disk, not a point source. If the Sun were simply a more brilliant version of Venus, all of it would rise in one pop. Instead, sunrise is defined as the moment when the Sun's upper edge breaches the horizon. Since the solar disk is about ½° in diameter, its full disk takes between 2.5 and 3 minutes at mid-latitudes to clear the horizon. Similarly, sunset is the moment the trailing limb finally touches the western horizon. That adds another 2.5 to 3 minutes of sunshine at day's end. The result is a total of approximately 5 to 6 minutes of additional daylight. By the way, this is true for every day of the year, not just on the equinox.
As one approaches the Arctic at the time of the fall equinox, the Sun's angle of ascent becomes shallower and shallower. In Alert, Nunavut, the northernmost continuously inhabited place in the world, it takes more than 16 minutes from the moment of sunrise until the Sun clears the eastern horizon! At the equator — the opposite extreme — the Sun rockets straight up from the due-east horizon and extricates itself in just over 2 minutes.
THE EARTH'S AIR
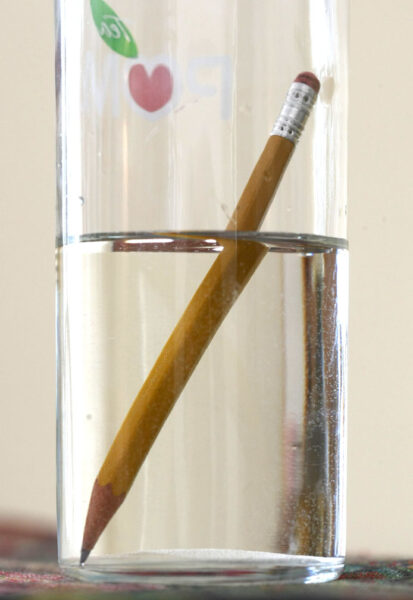
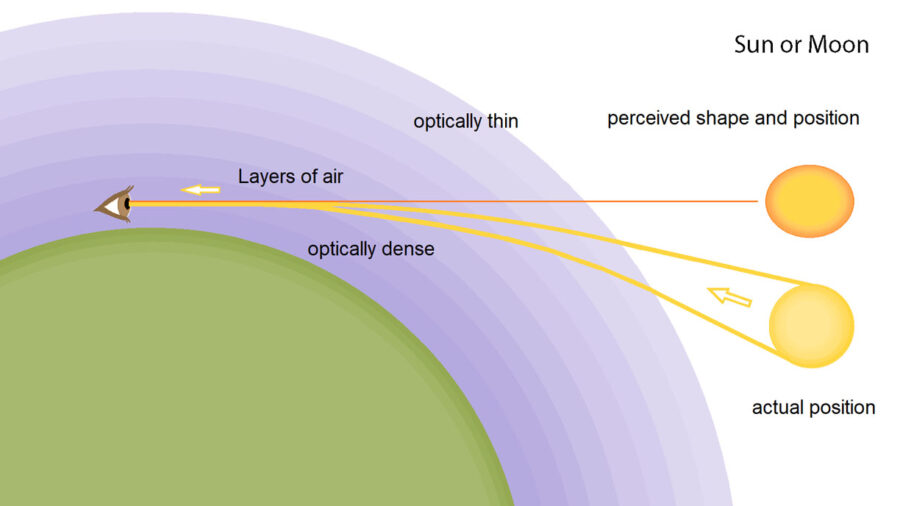
Adding to the complexity is the fact that Earth has air. Consider atmospheric refraction, in which light rays are bent when they pass from a less dense medium (outer space) into a more dense medium (Earth's atmosphere). A familiar example is the "broken" straw sticking out of a glass of water. Light from the top of the straw travels directly to our eyes, while light from the underwater part is refracted (bent) and travels in a slightly different direction, making it look as if it's fractured.

Bob King
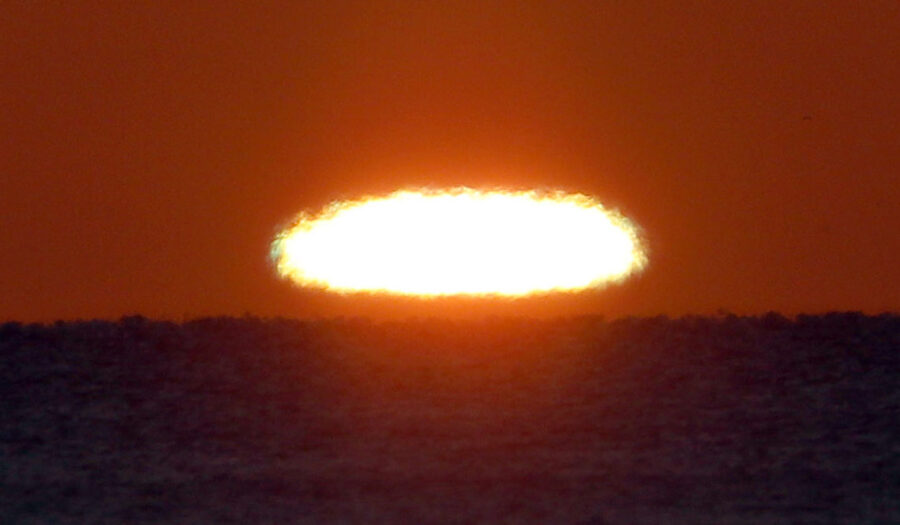
As the Sun approaches the horizon, air density rapidly increases, making refraction effects much stronger along the bottom edge of the solar disk compared to the top. The difference bends or "lifts" the bottom half of the solar disk into the top half, flattening an otherwise circular Sun into an oval.
Sciencia58 / CC BY-SA 4.0
Even before the Sun has physically risen in the morning, refraction elevates its upper edge, causing it to appear nearly 3 minutes (at mid-latitudes) beforehand. Likewise, the actual Sun sets several minutes before its refracted light does. If you were to remove Earth's atmosphere at sunset, sunlight would disappear the moment the entire solar disk sets.
So, we'll need to add another 5 to 6 minutes of daylight to the equinox due to Earth's atmosphere. Even if we were to imagine a hypothetical point at the center of the solar disk instead of the full Sun, atmospheric refraction would also lift it into view earlier and hold onto it later just like all celestial sources.

Stellarium
EQUAL LIGHT ON THE EQUILUX
Are days and nights ever 12 hours apiece? Yes! Well, close. This occurs at the equilux, a delightful word that derives from the Latin equi (equal) and lux (light). While the equinox occurs across the planet at the same moment, the equilux varies according to latitude.
In the Northern Hemisphere, it occurs several days after the autumnal equinox (on September 25th or 26th at mid-northern latitudes) and several days before the vernal equinox; in the Southern Hemisphere, it's the other way around.
At the equator, day and night are never exactly equal — daylight always exceeds night by 6 to 8 minutes due to the Sun's large apparent size. At the same time, though, day and night are nearly equal every day of the year.
| City | Latitude | Approximate date of equilux |
| Anchorage, Ak. | 61° | Sept. 25 |
| Calgary, Alberta | 51° | Sept. 25 |
| Champaign, Ill. | 40° | Sept. 26 |
| New Orleans, La. | 30° | Sept. 27 |
| Honolulu, Hawai'i | 21° | Sept. 28 |
| San José, Costa Rica | 10° | Oct. 4 |
| Bogotá, Colombia | 5° | Oct. 19 |
| Quito, Ecuador | 0° | Never |
Data from Stellarium and other sources
While the equilux concept is great in principle, a perfect balance of day and night isn't possible from many locations because daylight is decreasing at the rate of 2 to 3 minutes per day, not minute by minute. For that reason day and night lengths often differ by about a minute. For example, in Detroit the equilux occurs on September 25th, when the time between sunrise and sunset is only about 13 seconds shy of 12 hours. In Phoenix it occurs on the same date, but daylight is a little more than a minute longer than night.
Isn't splitting hairs fun?
The equinox is a happy time to be a night-sky watcher. Insects retreat, and evening temperatures are cool and pleasant. To stand under a dark sky before 9 o'clock is a joy. During the summer many of us start observing at the very time we should be getting to bed. These chances occur because of Earth's tilted axis. As the Sun hastens south, the curtain of darkness drops incrementally earlier. Before you know it, the insatiable night will make sunshine a prized commodity.
Happy equinox and equilux indeed!

Comments
Post a Comment