The three-year-old is losing weight and complains of leg pains and weakness. The doctor's diagnosis is clear - Nitisha is underfed and malnourished.
But the treatment suggested is difficult to come by for her family - wholesome meals.
Like many people in Sri Lanka, this family from a tea estate village in Hanthana, in the centre of the country, have seen their finances collapse.
"We manage two meals a day and it's the same thing - rice with potatoes or lentils. We can't afford anything else," says Harshini, Nitisha's mother. For weeks, the family has not had milk or eggs, she added.
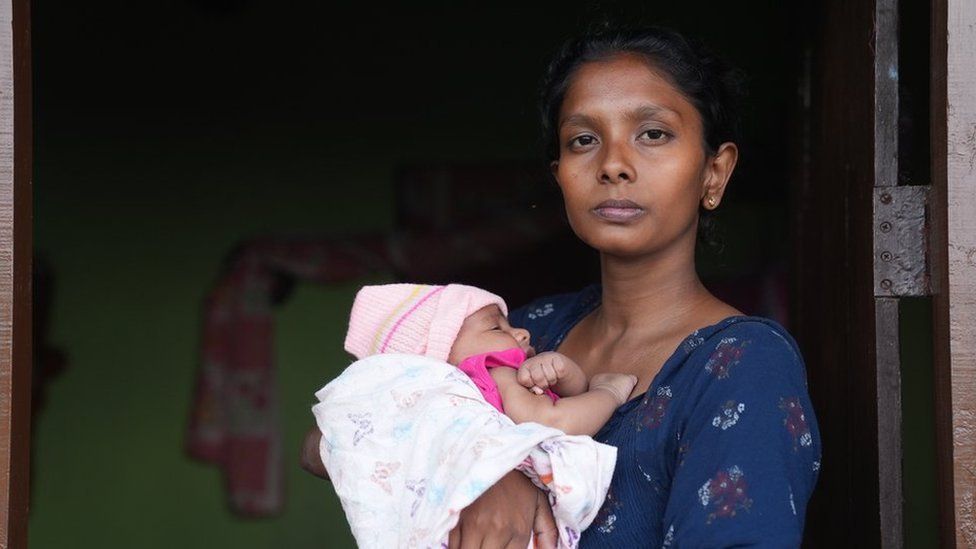
Harshini's younger daughter - just a month old - was also born underweight. The baby lacks thyroxine, a key growth hormone. The child joins the growing list of infants born with low birth weight - a direct impact of depleting gestational nutrition.
Food has been at the centre of Sri Lanka's economic crisis. Incomes are shrinking and food prices soaring. Families are forced to skip meals and go hungry.
Many children in Nitisha's village are becoming ill more often now. Doctors in the region say they are seeing more younger patients who are not getting enough to eat.
"Effects of malnourishment takes time to show," according to one doctor who asked not to be identified. "Currently most underfed children are using the stored reserves in the body, but a continued nutrition insufficiency would have long term impact."
UNICEF estimates approximately 56,000 children in the country are suffering from severe acute malnutrition.
Around a third of Sri Lankan households do not have a secure source of food and almost 70% are reducing meal sizes, according to the latest World Food Program figures.
Malnutrition and mothers
In Hanthana, 24-year-old Kanchana is in her fourth month of pregnancy and is expecting twins.
"With the twins I often get hungry, so I eat rice. Fish, eggs, fruits is better but expensive. We have to choose between paying for the tests and medicines or buying expensive food."
In another village a few kilometres away, we met Devi. She is pregnant with her second child but is severely anaemic and underweight. Options to improve her health are limited - a rice meal and free vitamin supplements from the government clinic.
"I wanted my second pregnancy to be healthier, but this is worse. Doctor says my child's development will be affected if I don't eat well."
The situation is precarious. The BBC spoke to 10 pregnant women in the area. Everyone was looking for assistance to go about their daily life. A government programme providing nutritional packets for pregnant women was suspended last year due to a lack of funds.
It restarted last month, but only a few have received the benefit.
"Many of us have applied for it, but almost half my pregnancy period is over and I haven't received even one packet," Devi said.
Christian Skoog, Unicef's country representative in Sri Lanka, said: "The mothers are not as nourished or as well-fed as they were before. It was already an issue, and it has gotten worse. Low birth weight is a big issue in Sri Lanka because women do not get enough nutrition during pregnancy or during gestation."
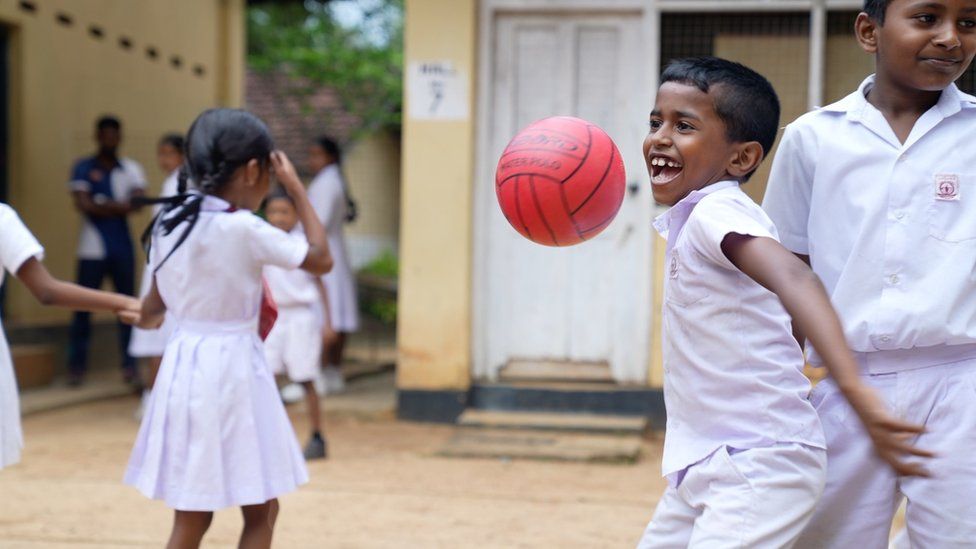
Hungry school children
"Most of these children, from primary grades, were coming to school without eating anything," according to Anoma Sriyangi Dharmawardhane, Vice Principal of Horawala Maha Vidyalaya in Mathugama in Southern Sri Lanka. "Daily, at least 20-25 children were fainting during school assembly three to four months ago".
The school started offering porridge and a midday meal programme with support of parents who volunteered to cook. It relies on donations to continue the program.
Community kitchens and food handouts like these are helping to fill the gap in parts of Sri Lanka, but still many children are going hungry.
"At least 20% of children get no breakfast and go to school [on an] empty stomach," according to S Visvalingam, President of the Food First Information & Action Network (FIAN), Sri Lanka.
For the last six months, FIAN has been organising food programmes for primary and secondary school children.
Mr Visvalingam said more students are dropping out of school, particularly in the worst-affected tea plantations areas in north and east Sri Lanka.
"These school food programmes, an assured meal a day, are helping get these children back to schools," he said.
"The food programmes are helping, saving lives and preventing things from getting worse. But it is still a stop-gap measure," said Mr Skoog.
After initially denying it, Sri Lankan government officials have acknowledged the growing crisis of acute malnutrition. Recent data from the health ministry's family health bureau showed stunting, low height for age, wasting and low weight-for-height among children has gone up significantly in the last one year.
In October, the government said it would double its initiative to give out free lunches at school and hand out supplements for toddlers.
However, Mr Visvalingam warns that Sri Lanka's problems are likely to get worse before they get better.
"I don't think [the] financial crisis can be resolved in the short term, and through this period the problem of nutrition is only going to get worse," he said.

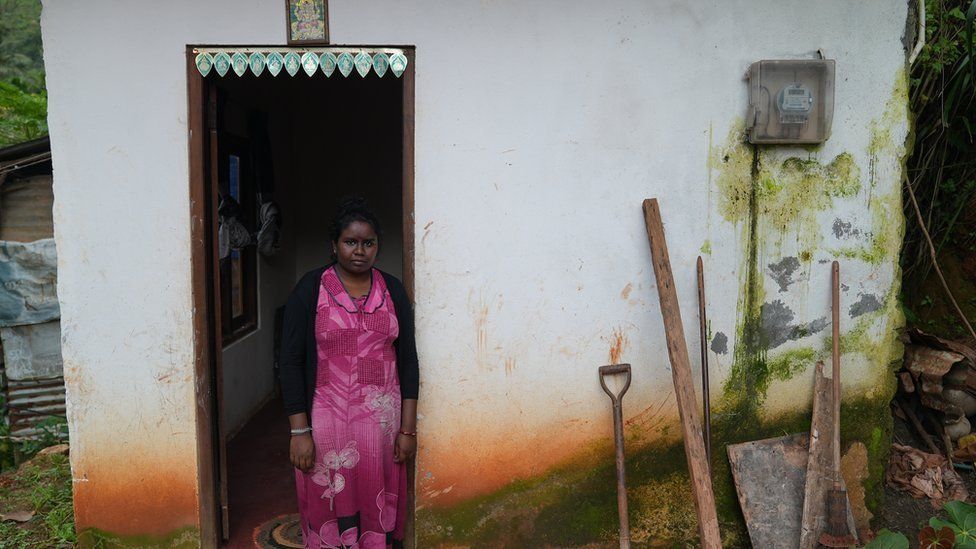

Comments
Post a Comment