From:- Space.com
Edited by: Amal Udawatta
While our ability to view distant worlds with advanced telescopes has come a long way in a short time, we can still only photograph a tiny fraction of the planets throughout our cosmos with the technology we have today.
However, astronomers in Hawaii just spotted a pair of exciting discoveries — a huge exoplanet and a brown dwarf — using Japan’s Subaru Telescope, which sits atop Mauna Kea, a dormant volcano on the Big Island of Hawaii.
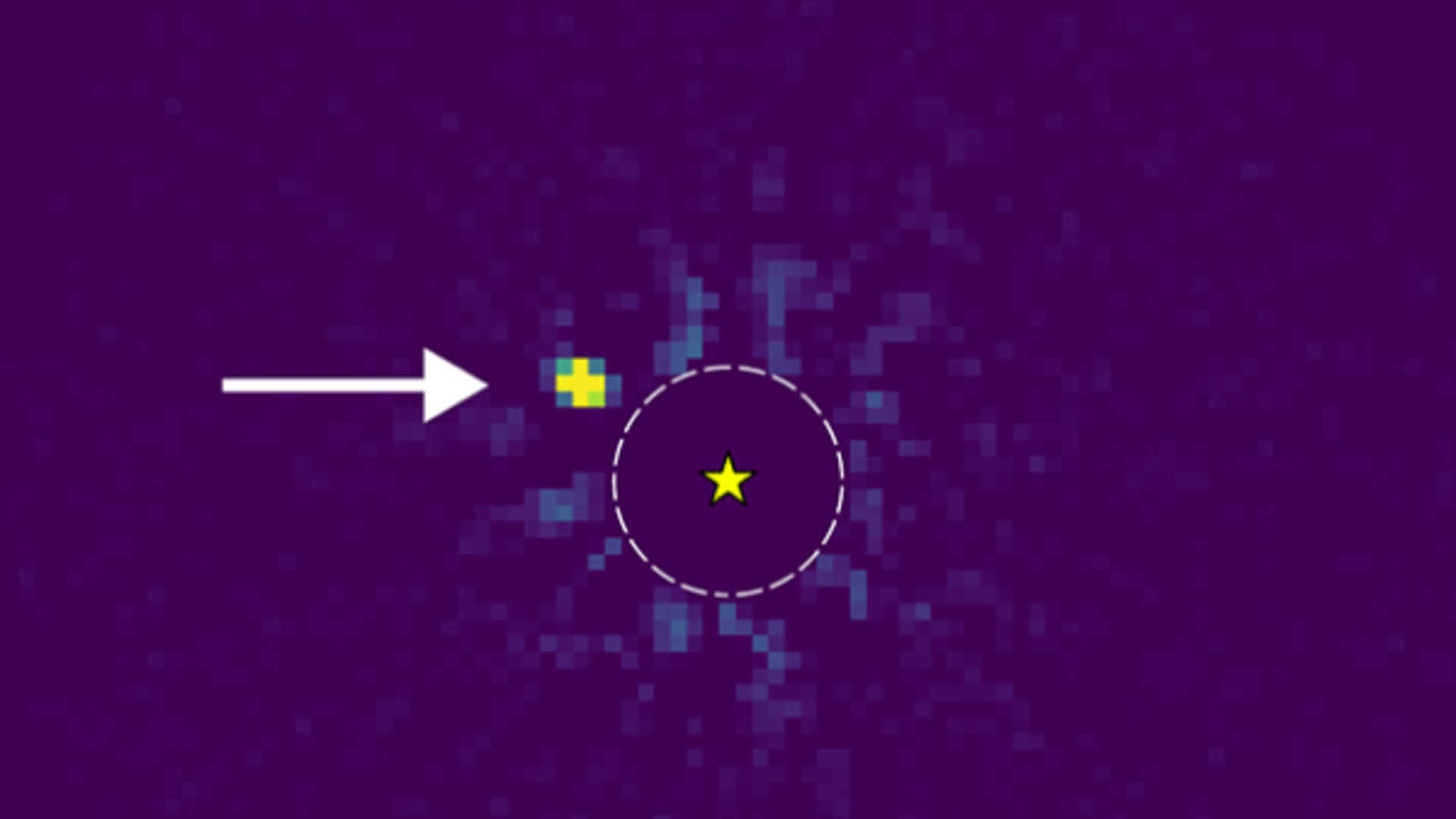
The exoplanet that the astronomers found is called HIP 54515 b. It's 271 light-years away from Earth and orbits a star in the Leo constellation. NAOJ says the planet is almost 18 times the mass of Jupiter and that it orbits its star from a vantage point that’s roughly the same as Neptune's distance from the sun.
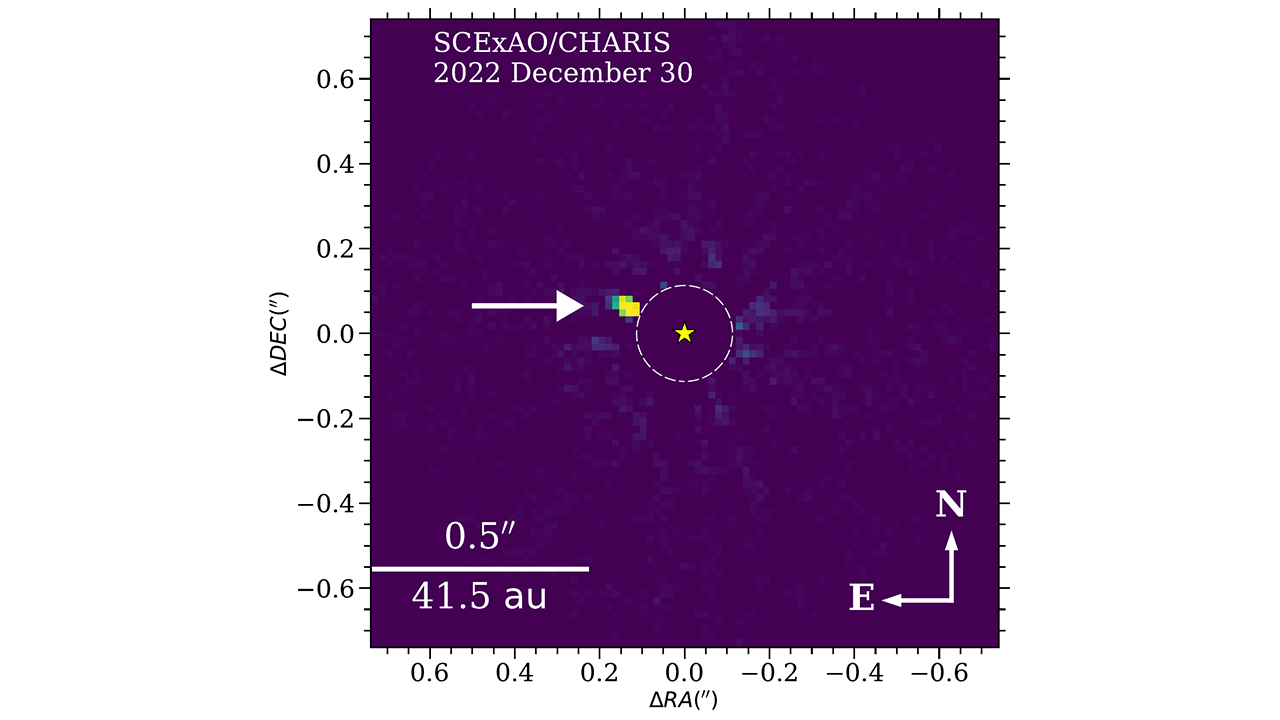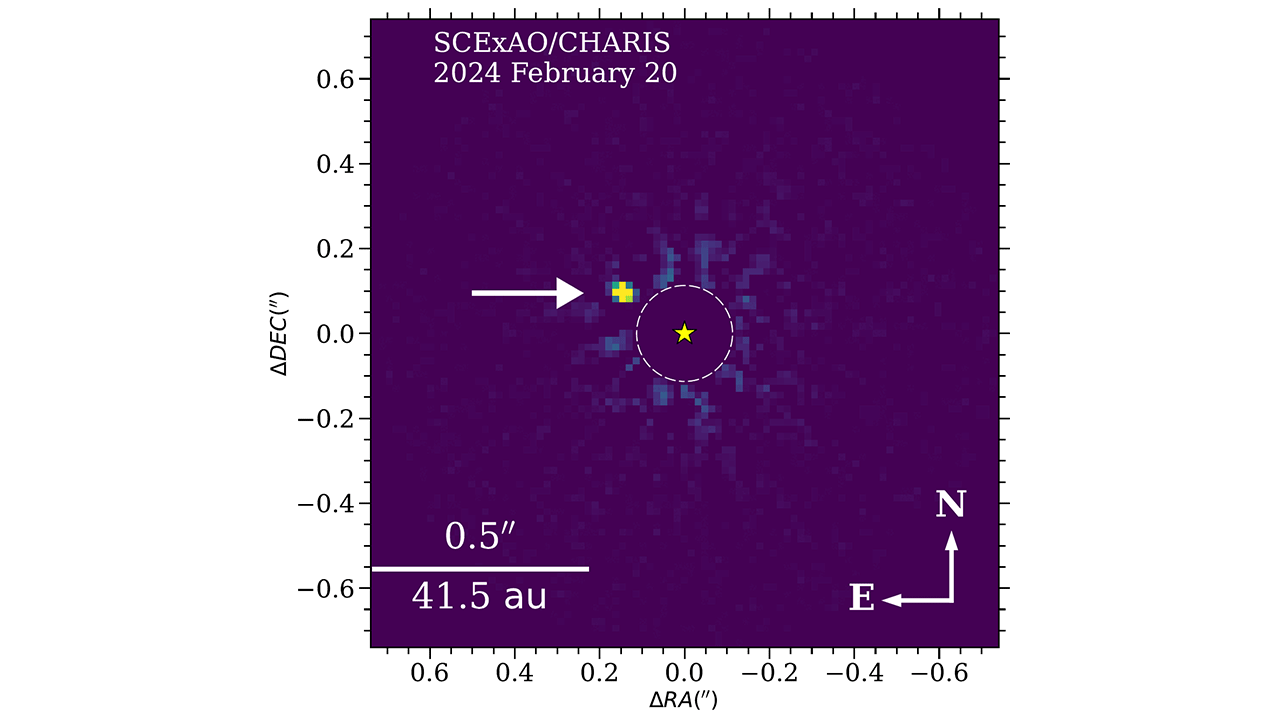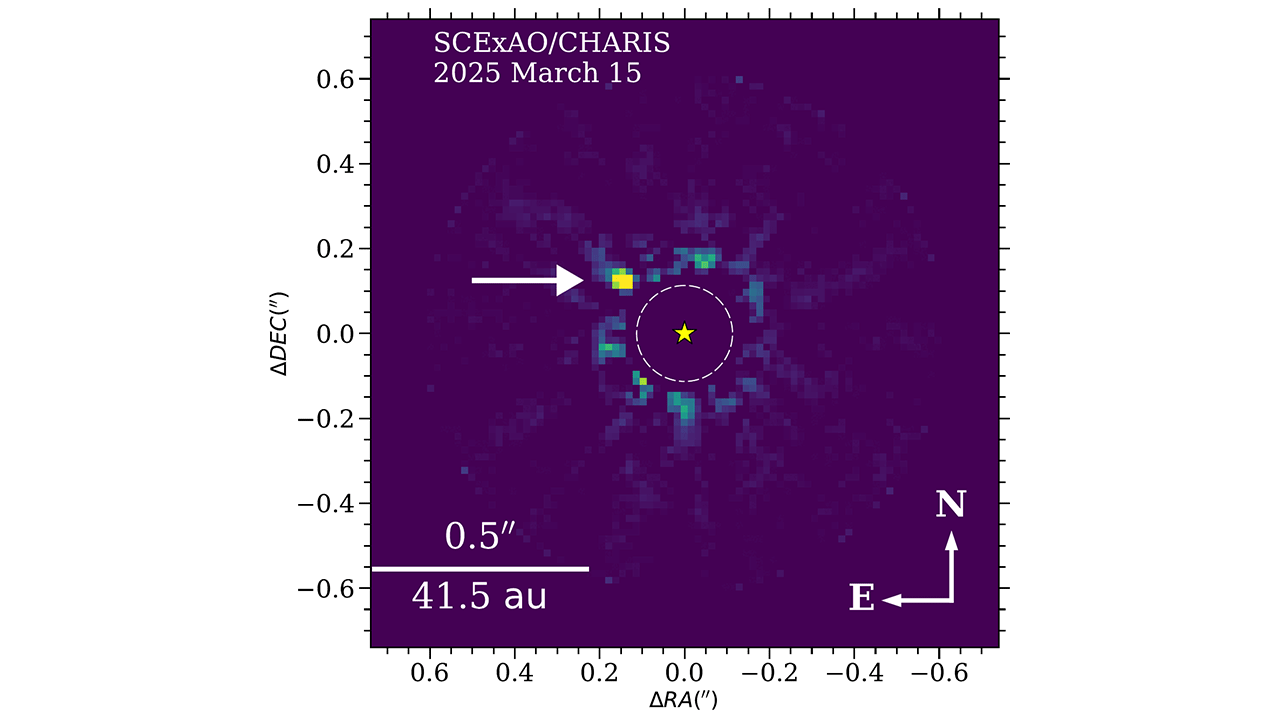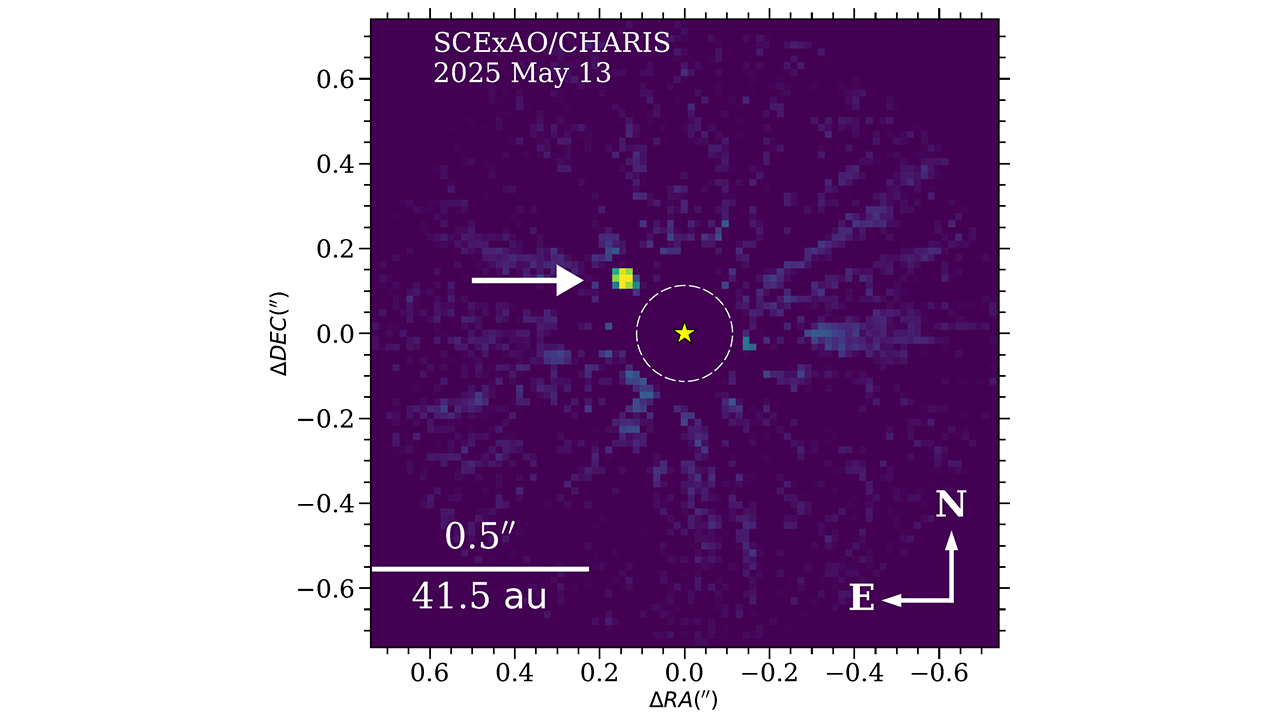
The brown dwarf, called HIP 71618 B, is 169 light-years away in the Bootes constellation. The term "brown dwarf" refers to a curious celestial object that has a mass somewhere between a planet and a star. Scientists often call brown dwarfs "failed stars," because these objects form in a similar way to stars but never accumulate quite enough mass to make the cut.
The discovery of the brown dwarf is especially exciting, because it has the right properties to test out NASA's new Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, which will launch in 2026 or 2027.
To test the Roman Space Telescope, NASA needs an object with pretty tight specifications. NAOJ says this brown dwarf checks all the boxes. "Roman will carry out a technology demonstration to test coronagraph systems that future telescopes will need to photograph Earth-like planets around other stars — planets that are ten billion times fainter than their host stars," NAOJ wrote.

So, with this new discovery, NAOJ says, Roman will have the right candidate for a technology demonstration.
Comments
Post a Comment