Millions of people across the UK and beyond have celebrated the coronation of King Charles III - a symbolic ceremony combining a religious service and pageantry.
The ceremony was held at Westminster Abbey, with the King becoming the 40th reigning monarch to be crowned there since 1066. Queen Camilla was crowned alongside him before a huge parade back to Buckingham Palace.
Here's how the day of splendour and formality, which featured customs dating back more than 1,000 years, unfolded.
King's Procession to the abbey
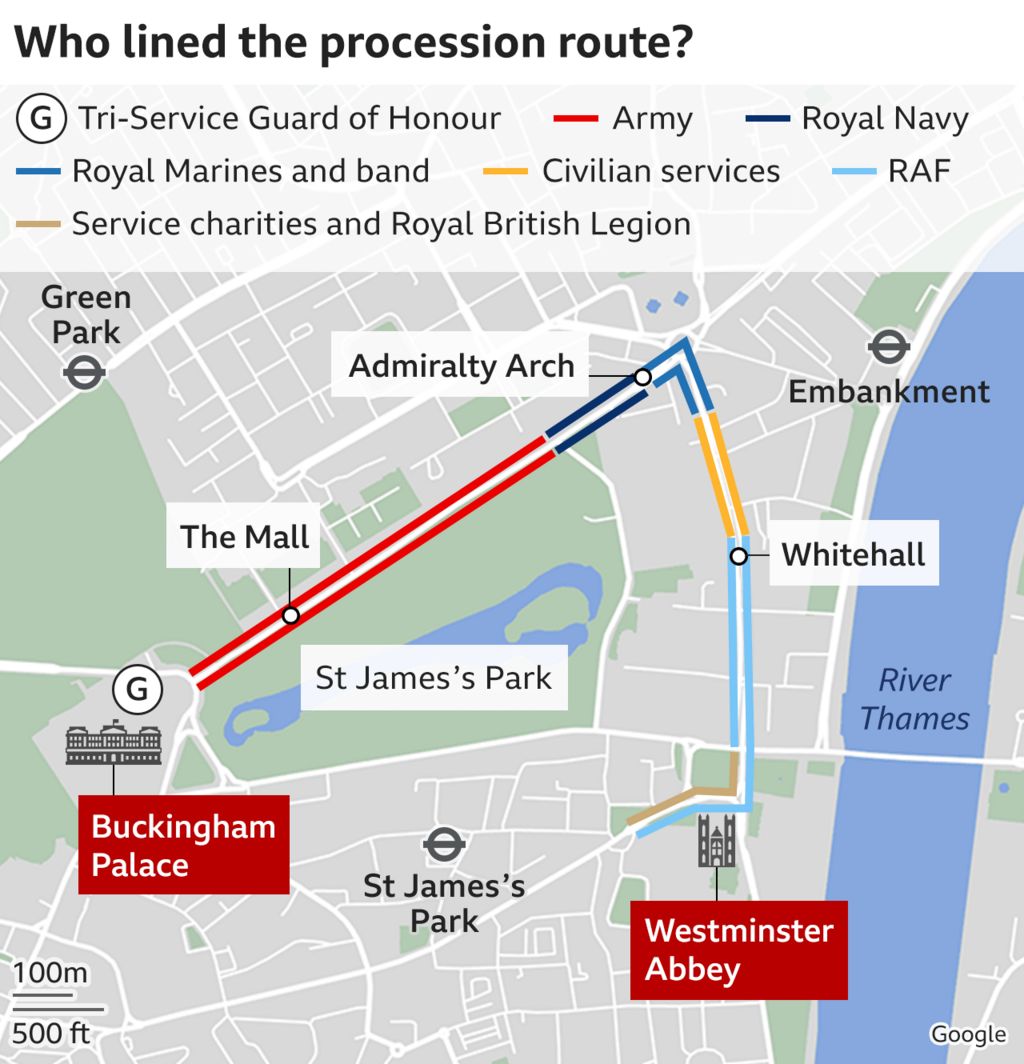
The formal celebrations started with a procession from Buckingham Palace to Westminster Abbey at 10:20 BST.
In a break from tradition, King Charles and Queen Camilla were in the Diamond Jubilee State Coach rather than the older, more uncomfortable, Gold State Coach.
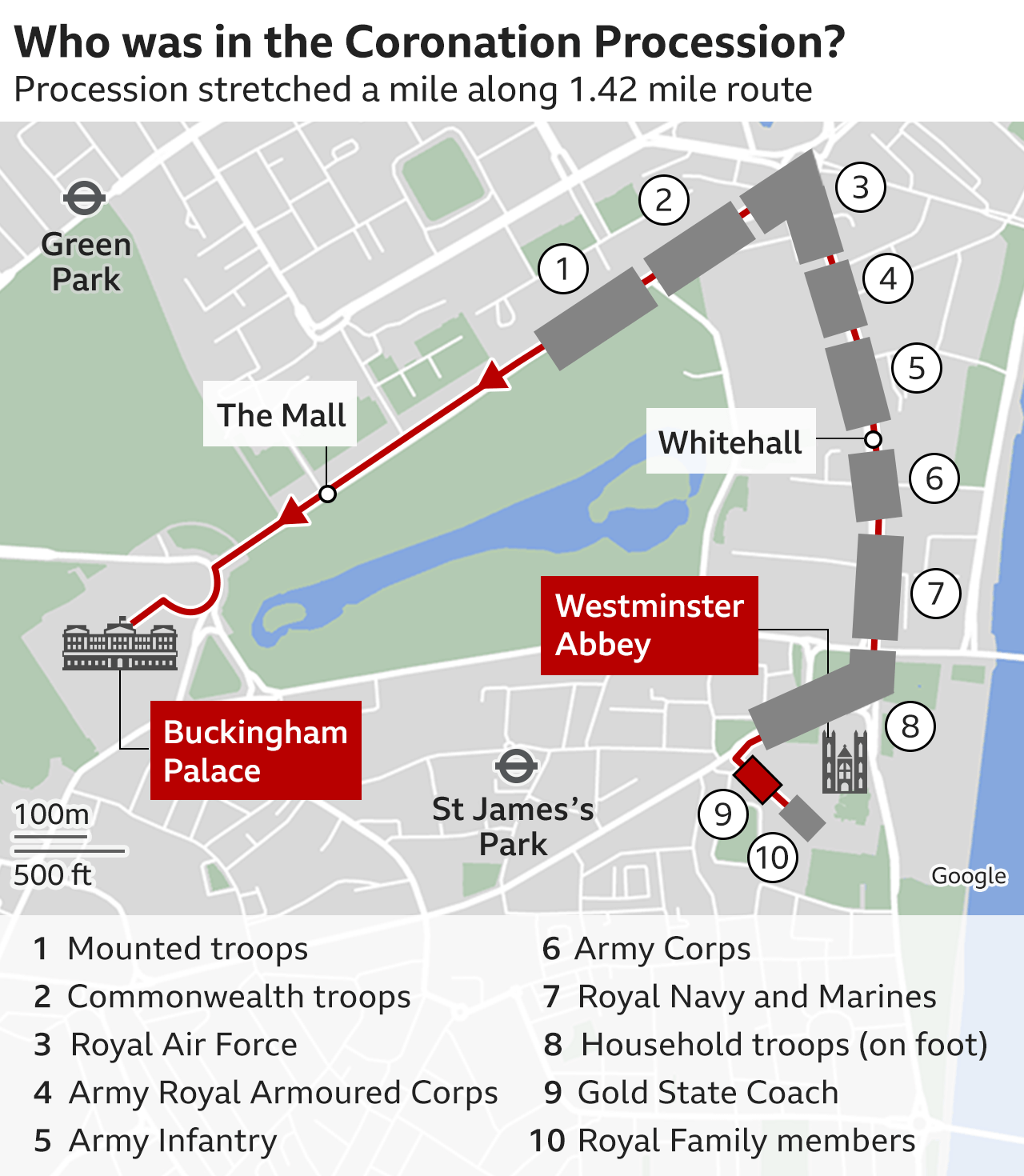
The procession moved along The Mall to Trafalgar Square, then down Whitehall and Parliament Street before turning into Parliament Square and Broad Sanctuary to reach the Great West Door of Westminster Abbey.
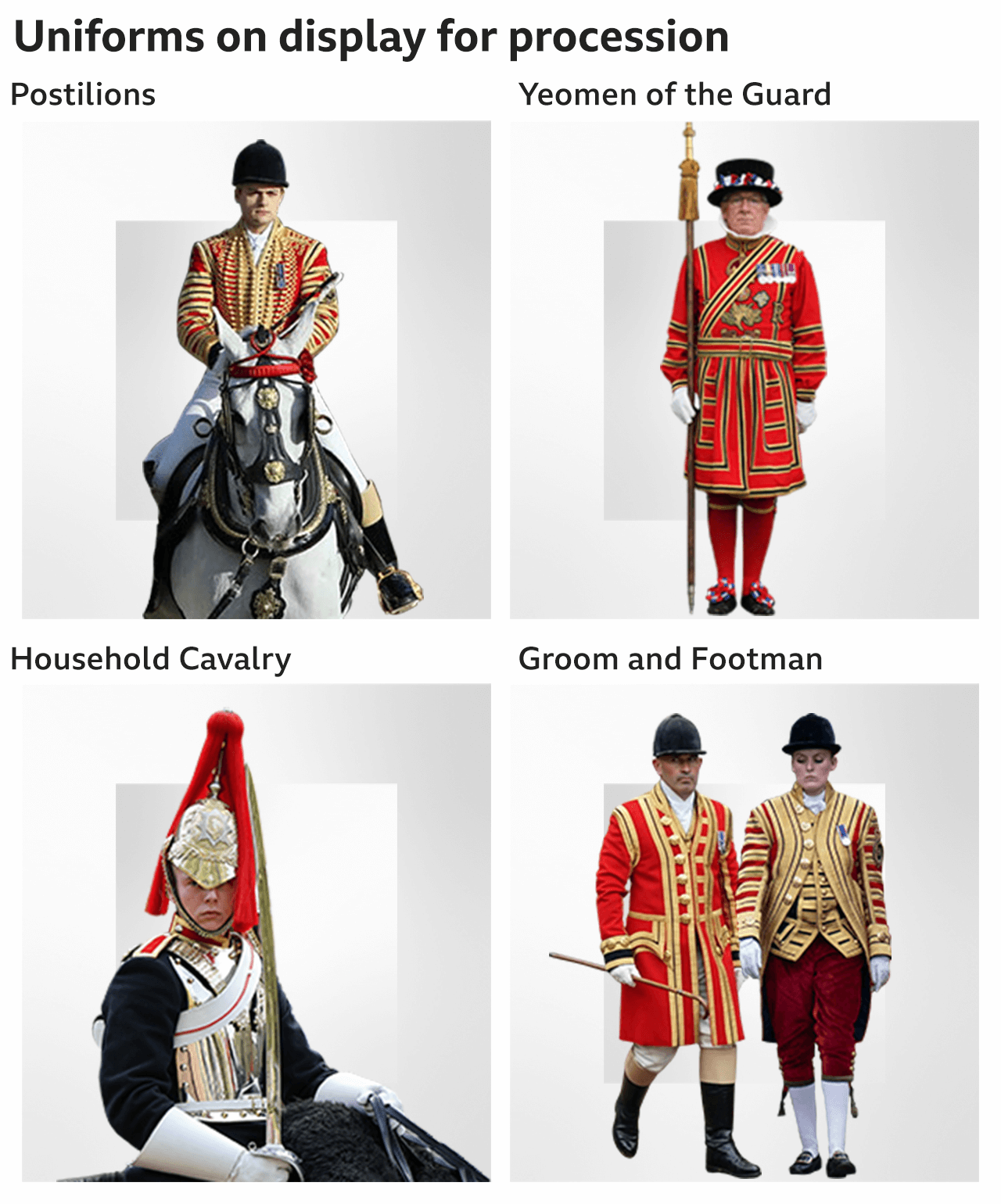
Outside the palace gates, there was a Guard of Honour, comprising about 160 members of the three armed services, with another 1,000 personnel lining the route.
Almost 4,000 invited guests, including armed forces veterans and NHS and social care staff, were in stands outside Buckingham Palace, with thousands more people in viewing areas along the route and official screening sites nearby.
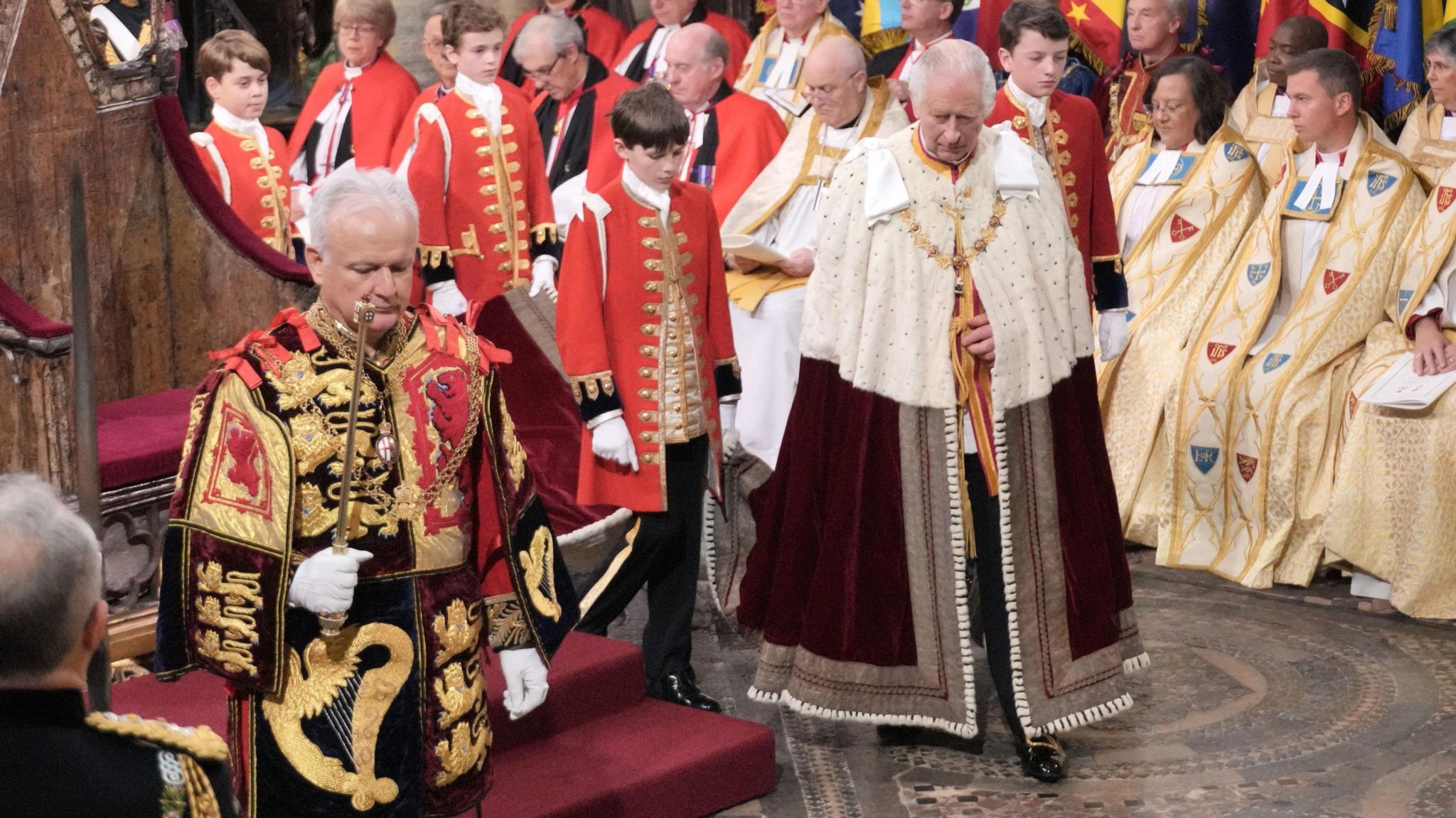
Westminster Abbey arrival
More than 2,200 people from 203 countries were in Westminster Abbey, with processions there before the King arrived involving faith leaders and representatives from some Commonwealth countries.
They were accompanied by the governors general and prime ministers, including UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak who also gave a reading in the service.
The King arrived at the abbey wearing a red velvet robe of state. Underneath he was wearing trousers rather than the more traditional breeches and silk stockings worn by kings before him.
The ceremony began at 11:00 and was punctuated with music selected by the King, with 12 newly commissioned pieces, including one by Andrew Lloyd Webber, and Greek Orthodox music in memory of the King's father, Prince Philip.
The King's grandson, Prince George, was among the pages, alongside Camilla's grandchildren, Lola, Eliza, Gus, Louis and Freddy.
Some of those who walked ahead of the King through the abbey carried the regalia placing items on the altar until they were needed.
What is the regalia?
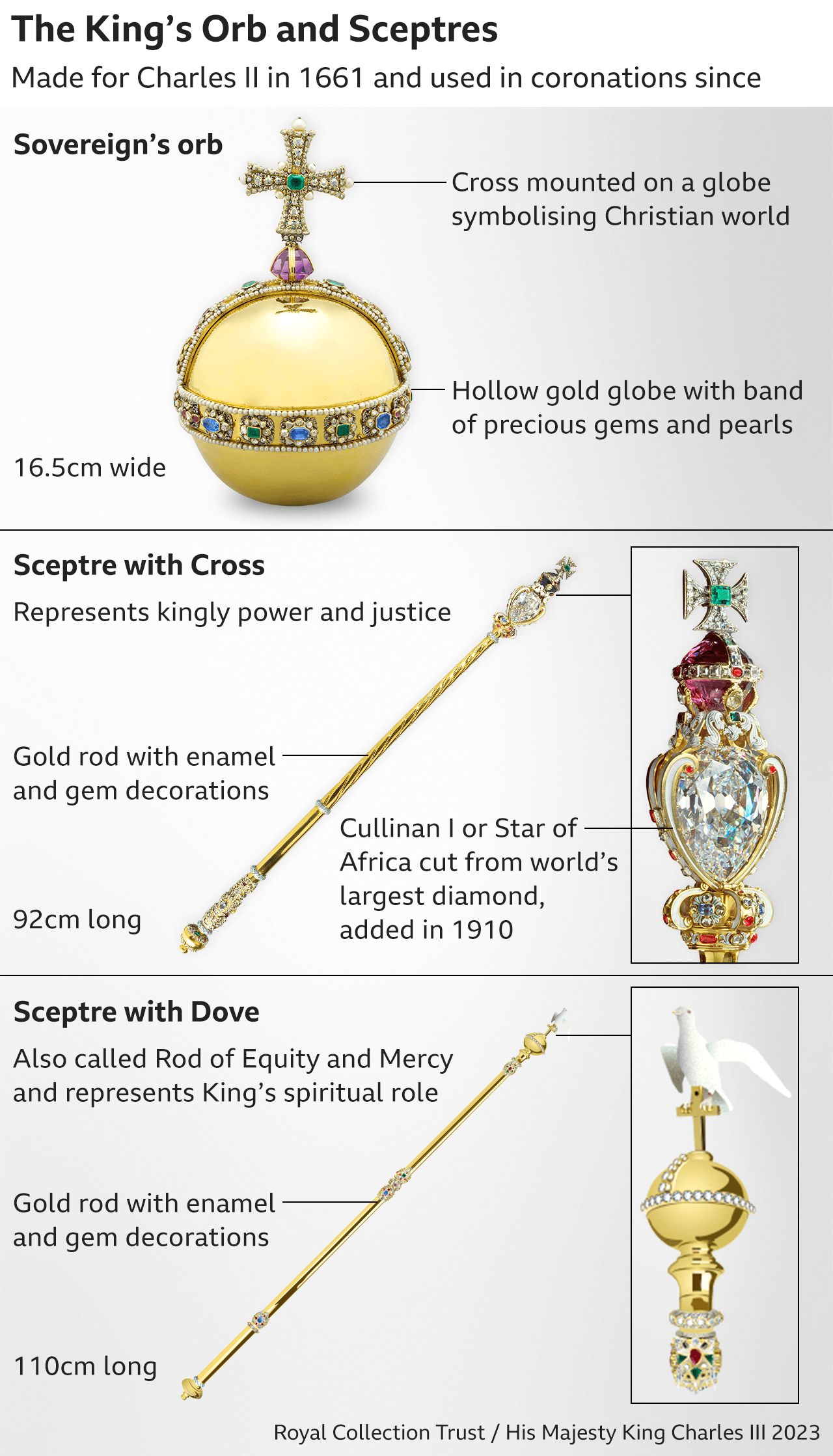
The UK is, according to the Royal Family website, the only European country that still uses regalia - the symbols of royalty like the crown, orb and sceptres - in coronations.
The individual objects symbolise different aspects of the service and responsibilities of the monarch.
Charles was presented with the Sovereign's Orb, the Sovereign's Sceptre with Cross, and the Sovereign's Sceptre with Dove and other items during the ceremony.
And Camilla was presented with the Queen Consort's Rod with Dove and the Queen Consort's Sceptre with Cross - mirroring the King's sceptres.
There were several stages to the service, which lasted a little under two hours, with female clergy and religious leaders from other faiths playing an active part for the first time.
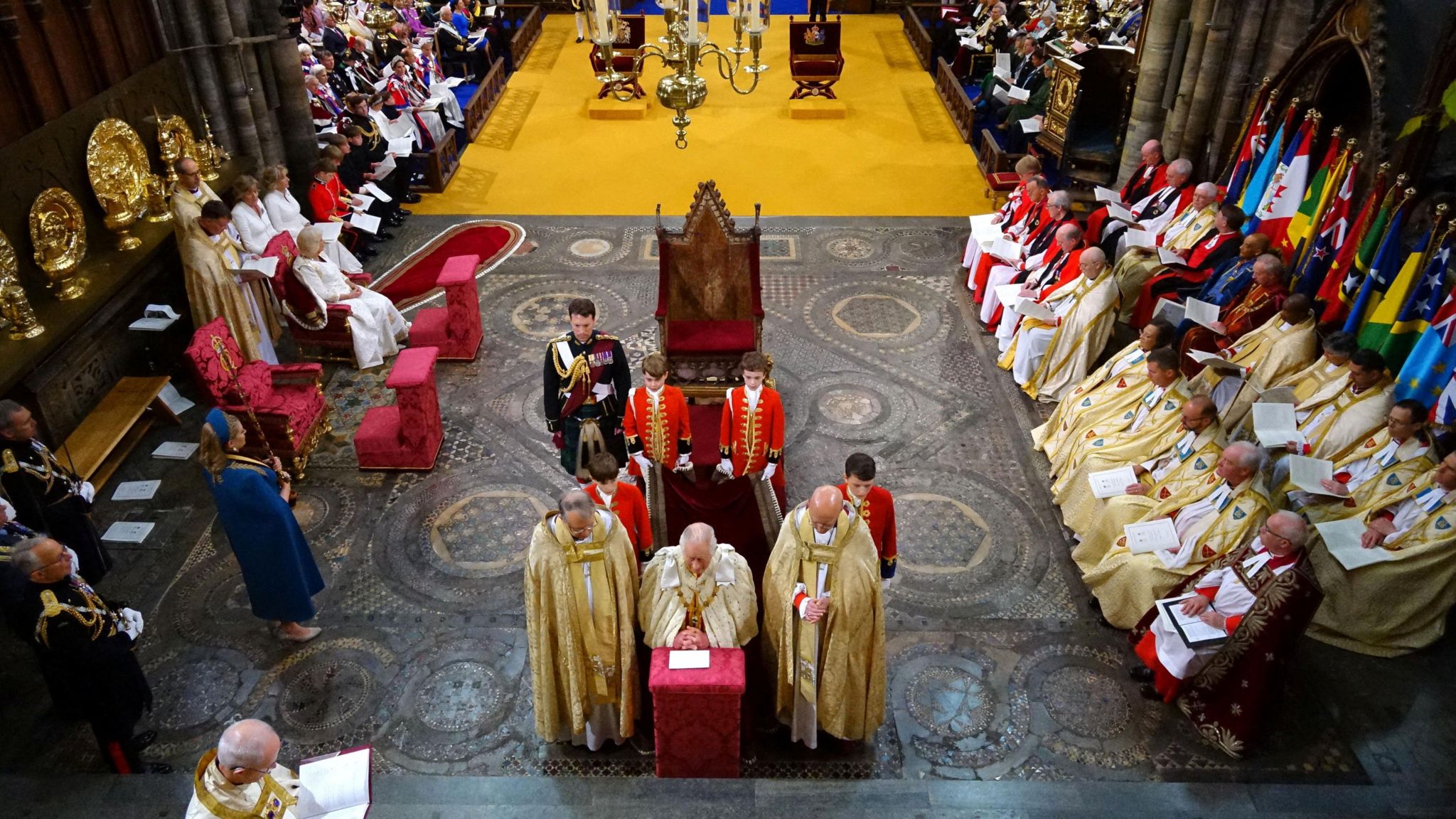
Stage one: The recognition
King Charles was presented to "the people" - a tradition dating back to Anglo-Saxon times. Standing beside the 700-year-old Coronation Chair, the King turned to face the four sides of the abbey and be proclaimed the "undoubted King" before the congregation was asked to show their homage and service.
Archbishop of Canterbury Justin Welby made the first declaration and the congregation shouted "God Save the King!" and trumpets sounded after each recognition.
The Coronation Chair, also known as St Edward's Chair or King Edward's Chair, is believed to be the oldest piece of furniture in the UK still used for its original purpose. Charles was the 27th monarch to be crowned in it.
It was originally made by order of England's King Edward I to enclose the Stone of Destiny, which had been taken from near Scone in Scotland.
The stone - an ancient symbol of Scotland's monarchy - was returned to Scotland in 1996 but was transferred back to London for use in the service.
During the Coronation, the oak chair was placed in the centre of the historic medieval mosaic floor known as the "Cosmati pavement", in front of and facing the high altar, to emphasise the religious nature of the ceremony.
Stage two: The oath
The Archbishop of Canterbury acknowledged the multiple faiths observed in the UK by saying the Church of England would "seek to foster an environment in which people of all faiths may live freely" and then administered the Coronation Oath - a legal requirement.
He asked King Charles to confirm that he would uphold the law and the Church of England during his reign, and the King placed his hand on the Holy Gospel and pledged to "perform and keep" those promises.
The King also took the Accession Declaration Oath stating that he was a "faithful Protestant".
Stage three: The anointing
The King's ceremonial robe was removed and he sat in the Coronation Chair to be anointed, emphasising the spiritual status of the sovereign who is also the head of the Church of England.
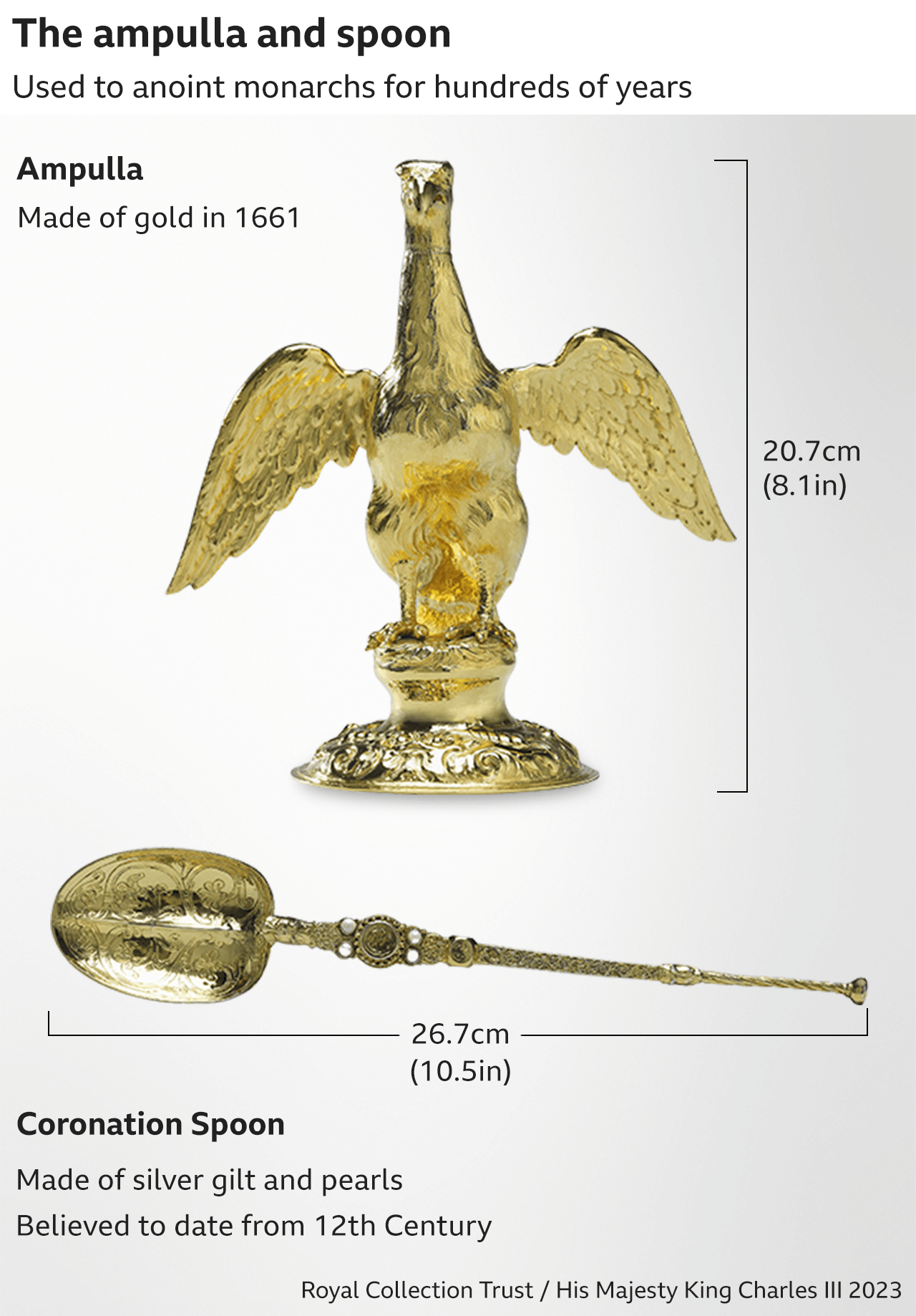
The archbishop poured special oil from the Ampulla - a gold flask - on to the Coronation Spoon before anointing the King in the form of a cross on his head, breast and hands.
The Ampulla was made for Charles II's coronation, but its shape harks back to an earlier version and a legend that the Virgin Mary appeared to St Thomas a Becket in the 12th Century and gave him a golden eagle from which future kings of England would be anointed.
The Coronation Spoon is much older, having survived Oliver Cromwell's destruction of the regalia after the English Civil War.
The oil itself was produced for the coronation using olives harvested from two groves on the Mount of Olives in Jerusalem, and consecrated at a special ceremony at the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in the city.
A screen concealed the King from view while he was anointed, because this is considered to be the most sacred part of the service.
Stage four: The investiture
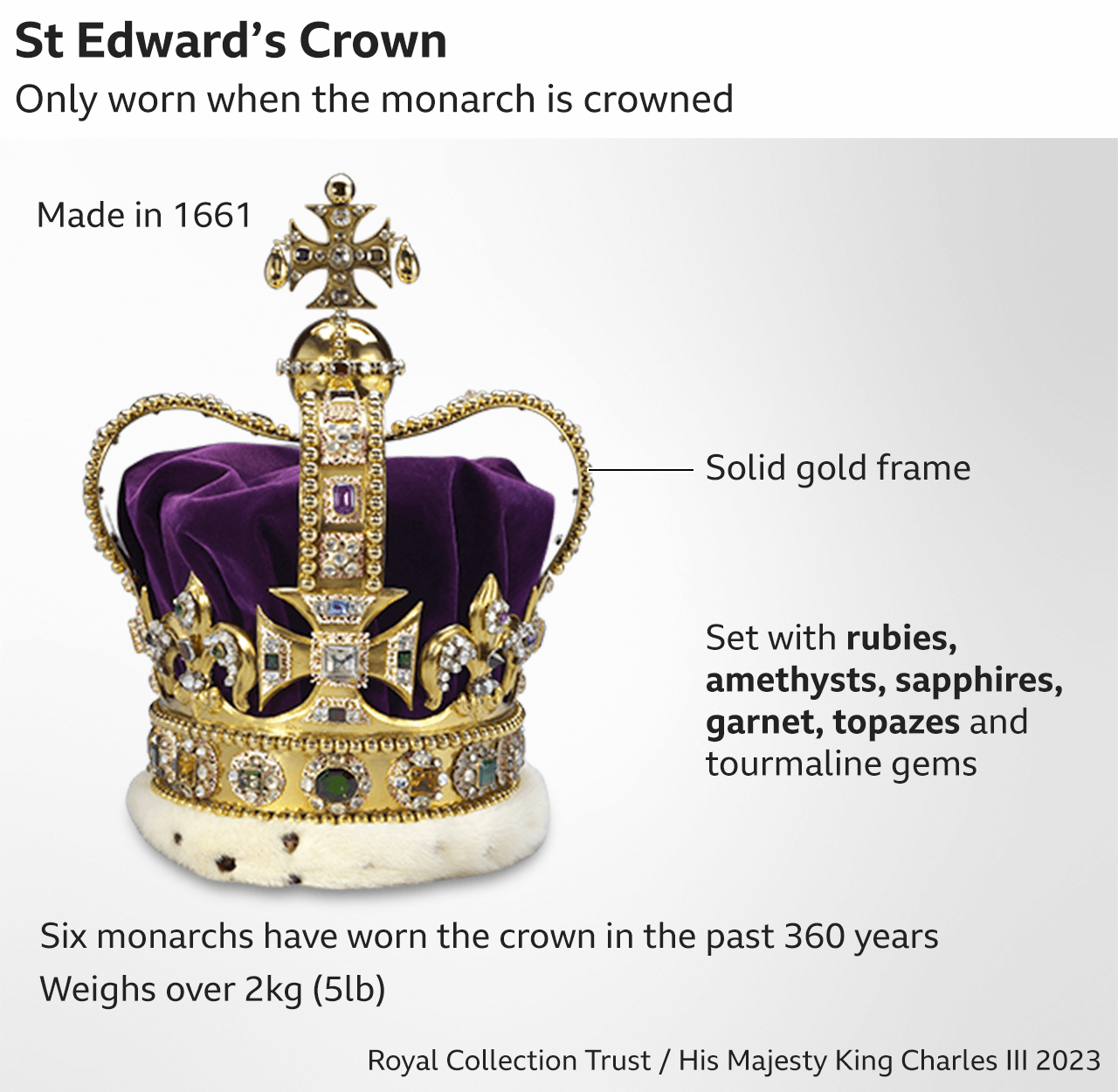
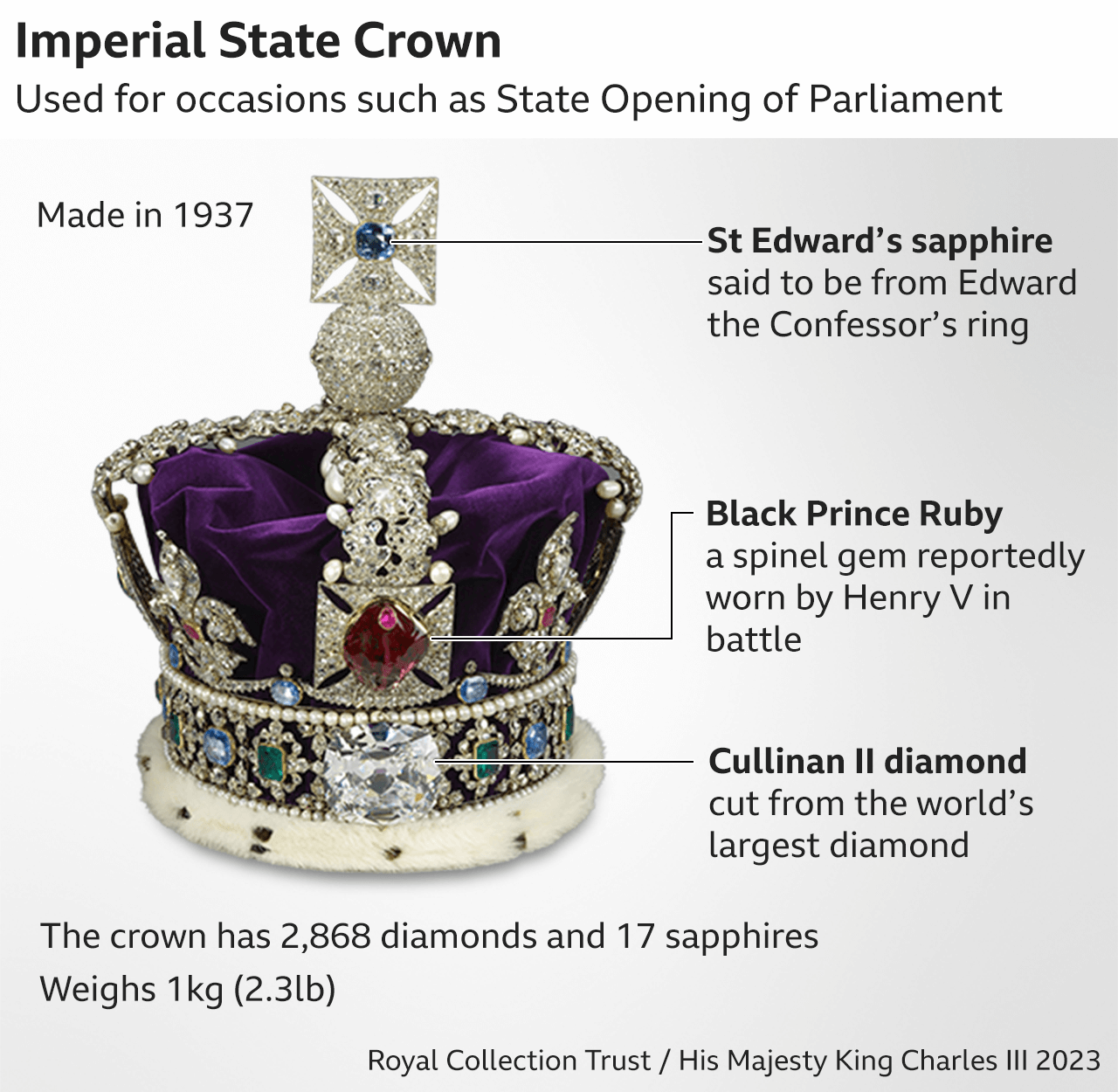
Literally the crowning moment - and the only time King Charles will wear St Edward's Crown in his life.
The crown is named after a much earlier version made for the Anglo-Saxon king and saint, Edward the Confessor, and said to have been used at coronations after 1220 until Cromwell had it melted down.
It was made for King Charles II, who wanted a crown similar to the one worn by Edward but even grander.
King Charles III was only the seventh monarch to wear it after Charles II, James II, William III, George V, George VI and Elizabeth II - who last wore it at her own coronation in 1953.
First the King was given a shimmering golden coat to wear called the Supertunica, and presented with items including the Sovereign's Orb, the Coronation Ring, the Sovereign's Sceptre with Cross and the Sovereign's Sceptre with Dove.
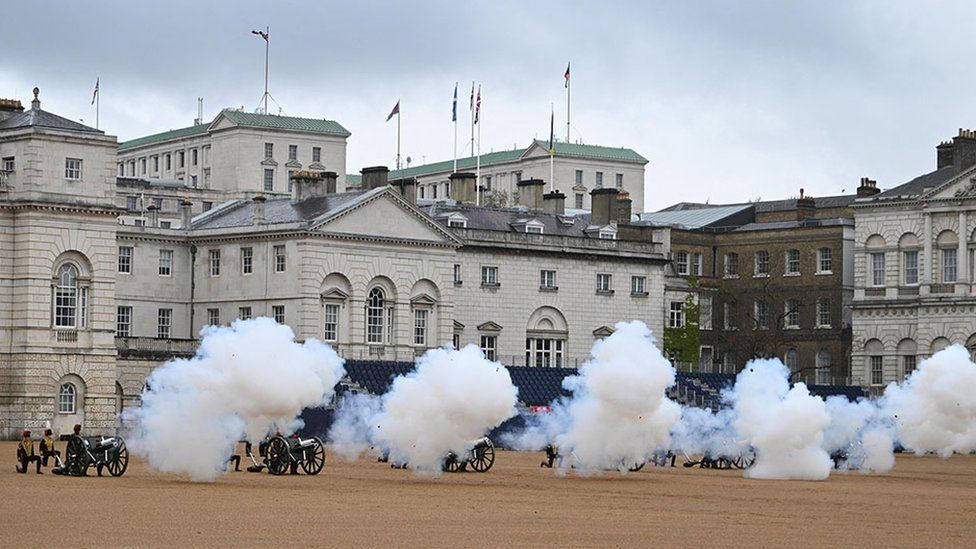
Then at 12:01 the archbishop placed St Edward's Crown on the King's head and the abbey bells rang for two minutes, trumpets sounded and gun salutes were fired across the UK.
A 62-round salute fired at the Tower of London, with a six-gun salvo at Horse Guards Parade. Twenty-one rounds were fired at a further 11 locations around the UK, including Edinburgh, Cardiff and Belfast, and on deployed Royal Navy ships.
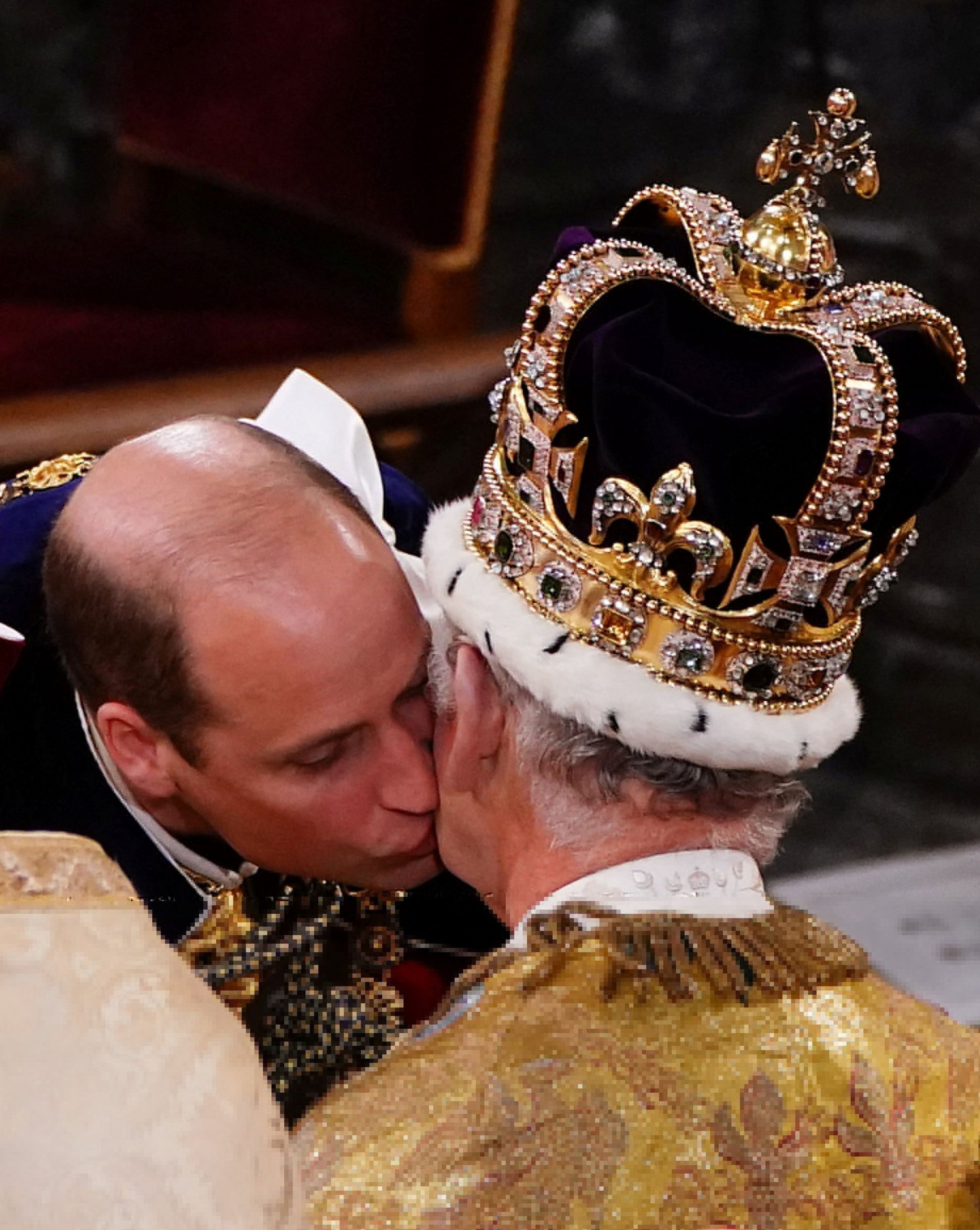
Stage five: The enthronement
The King then moved to his throne where, traditionally, a succession of royals and peers would have paid homage - but the Prince of Wales was the only person to do so this time.
Instead, the archbishop invited people in the abbey, and those watching and listening at home, to pledge allegiance by saying the words: "I swear that I will pay true allegiance to Your Majesty, and to your heirs and successors according to law. So help me God."
Crowning the Queen
After the homage, Queen Camilla was also crowned and enthroned - although she did not have to take an oath.
She was crowned with Queen Mary's Crown - originally made for Queen Mary's coronation alongside George V - but it was modified to remove some of the arches and reset with the Cullinan III, IV and V diamonds.
Communion
In the final part of the service the King and Queen took Holy Communion - the principal act of worship of the Christian church.
The departure
They then left their thrones and entered St Edward's Chapel behind the high altar - there Charles removed St Edward's Crown and put on the Imperial State Crown before joining the procession out of the abbey as the national anthem was played.
Coronation Procession to the palace
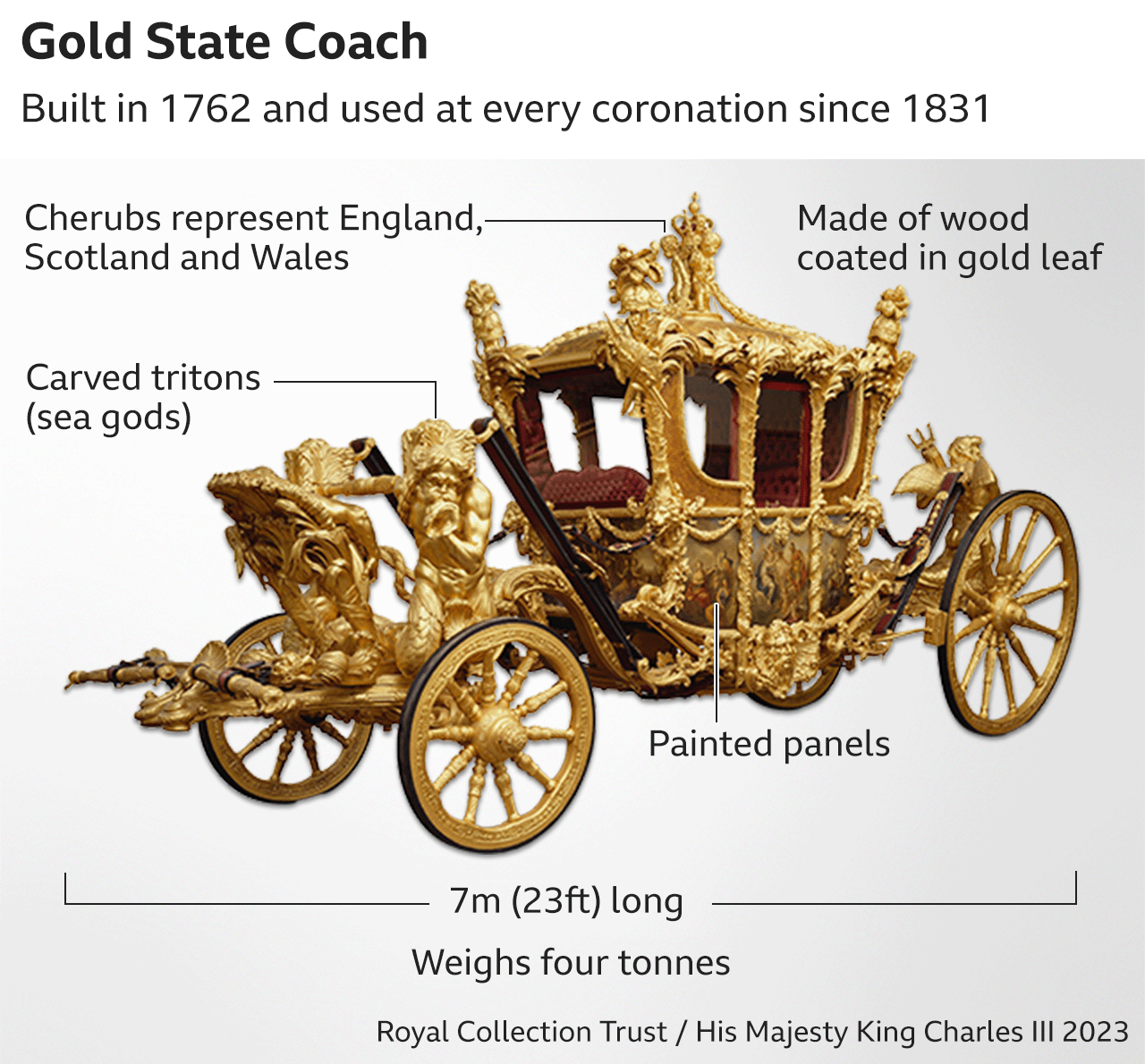
The King and Queen returned to Buckingham Palace along the reverse of the route by which they came, this time travelling in the 260-year-old Gold State Coach that has been used in every coronation since William IV's.
The Princess Royal was among those riding behind the coach, while the Prince and Princess of Wales and their three children, princes George and Louis and Princess Charlotte, were among the royals in the three carriages and first car following.
Nearly 4,000 members of the UK's armed forces took part in what the Ministry of Defence has called the largest military ceremonial operation of its kind for a generation.
They were joined by representatives from 39 Commonwealth countries and the British Overseas Territories. Most marched ahead of the King along the 1.42 miles (2.29km) route and, as the front of the procession reached the palace, the back was still at Downing Street.
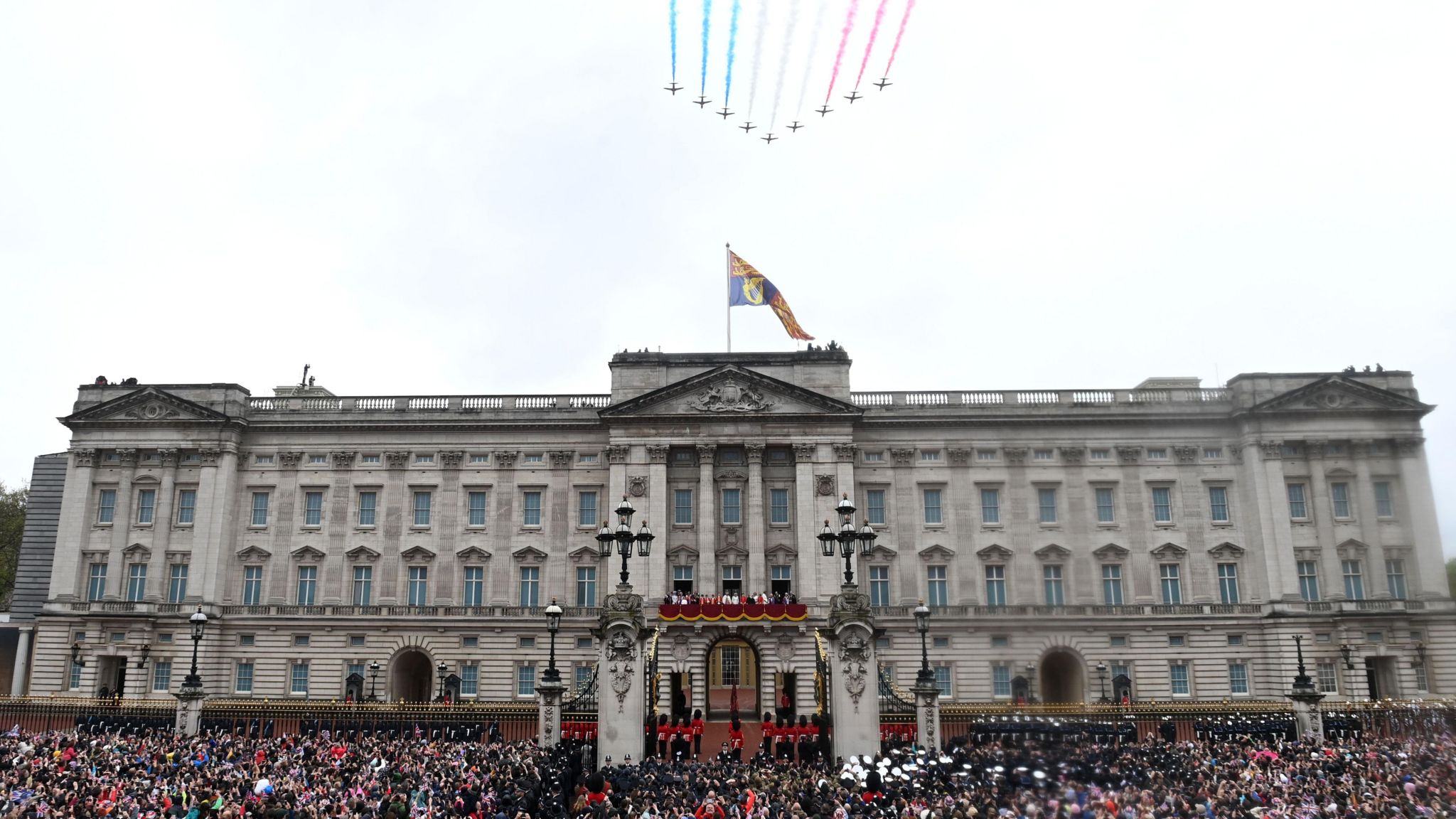
The King and Queen arrived at the palace shortly after 13:30 and received a Royal Salute and three cheers from the military personnel who had been on parade.
Buckingham Palace fly-past
It has become customary since the coronation of Edward VII in 1902 for the new monarch to greet the crowds in The Mall from the Buckingham Palace balcony - King Charles and Queen Camilla continued the tradition and appeared shortly before 14:30 with the royals who had taken part in the procession.
The day ended with a fly-past, although unsuitable weather conditions meant it was be limited to helicopters and the Red Arrows display team.
Written and produced by Chris Clayton, design by Lilly Huynh and Zoe Bartholomew, illustration by Jenny Law




















Comments
Post a Comment